WB4-2
Improvement of flux pinning force density characteristics of BaHfO3-doped SmBa2Cu3Oy films annealed at various temperatures
Dec.2 08:55-09:10 (Tokyo Time)
Department of Electrical Engineering, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8603, Japan1
Department of Electric and Electronics Engineering, Aichi Institute of Technology, Toyota 470-0392, Japan2
The high-temperature superconductor REBa2Cu3Oy (REBCO, RE = rare earth) shows an excellent superconducting property even under a high magnetic field [1]. In addition, the REBCO has a high critical current density Jc at a low temperature of 4.2 K, which is expected to be applied to NMR that generates a magnetic field ~ 45.5 T [2]. Therefore, further enhancement of Jc is required at a low temperature and in a high magnetic field where oxygen vacancy is considered to be effective in improving Jc. In fact, we reported that the addition of BaHfO3 (BHO) improved Jc in REBCO films at a low temperature, which could be due to the oxygen vacancy in the REBCO films [3]. In this study, the annealing temperature Ta was controlled to improve Jc of non-doped and BHO-doped SmBa2Cu3Oy (SmBCO) films at a low operating temperature.
Non-doped and BHO-doped SmBCO films were prepared on CeO2-buffered IBAD-MgO substrates by the pulsed laser deposition method. The films were processed at annealing temperatures Ta of 150-400 ºC in an oxygen atmosphere. Field dependences of the Jc were measured at 4.2 K with B//c-axis to calculate the flux pinning force density Fp.
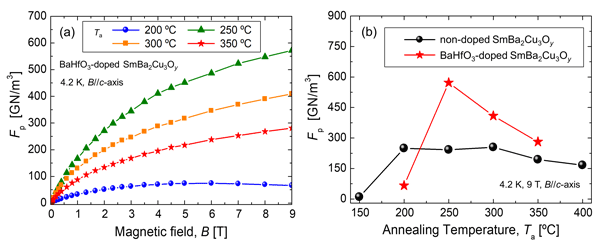
Fig. 1(a) shows field dependence of the Fp at 4.2 K of the BHO-doped SmBCO films annealed at Ta. The Fp was the highest at Ta = 250 ºC. Fig. 1(b) shows Ta dependence of the Fp of the non-doped and the BHO-doped SmBCO films at 4.2 K and 9 T. The maximum Fp of the BHO-doped films was 592 GN/m3 at Ta = 250ºC, which is 2.3 times higher than one of the non-doped films. In addition, a narrow range of Ta with high Fp of the BHO-doped films was confirmed, compared with the non-doped films. We will discuss the above results by analyzing whether the enhanced Jc of the BHO-doped films are due to flux pinning by the BHO phase or the oxygen vacancy.
This work was partly supported by JSPS (19K22154, 20H02682, 20K15217), JST-A-STEP, and NEDO. The IBAD-MgO substrates were provided by Dr. Y. Iijima of Fujikura Ltd.
Fig. 1. (a) Field dependences of the flux pinning force density Fp of the BaHfO3-doped SmBa2Cu3Oy films at 4.2 K processed at various annealing temperatures Ta. (b) Ta dependences of Fp of the non-doped and the BaHfO3-doped SmBa2Cu3Oy films at 4.2 K and 9 T.
Reference:
[1] Y. Shiohara et. al., J. J. App. Phys. 51, 010007 (2012).
[2] S. Hahn et. al., Nature 570, 496-499 (2019).
[3] S. Miura et. al., Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30, 084009 (2017).
Keywords: REBCO, artificial pinning center, coated conductor, critical current